Data Structures
- Documentation
- Feature Overview
- Data Structures
The Octree data structure is mapped to a one-dimensional array in order to have an efficient data structure on which the solver can act on in a performant way. An efficient representation of the elements and their neighbor relations is chosen. The fluid elements are mapped to a one-dimensional array and the neighboring relations are introduced by an additional connectivity array. The access of a neighbor element is performed by looking up the correct position of an element's link neighbor in the connectivity array, thus constituting an indirect access.
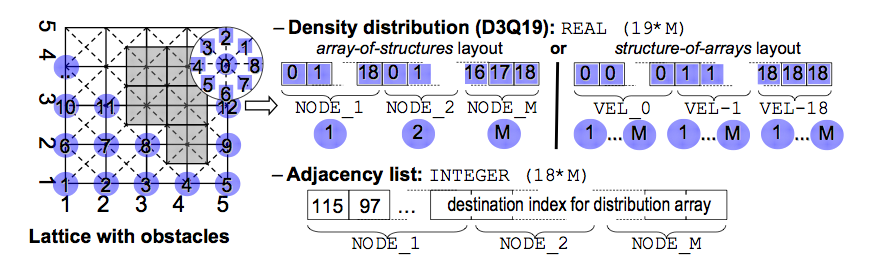
The different dependencies of each link in an element require a thorough treatment, when data is exchanged at domain boundaries. Only the links, which point outside the domain have to be sent to neighbor partitions, and the links pointing inwards have to be filled with valid values from these.
- Bibliography
-
Examples
- Weakly compressible flows
- Incompressible flows
- Tutorials
- Feature Overview
- Build and run Musubi